- Home
- Online Earning Site
- _What is Bitcoin
- _What is SEO
- __Branded and Non-Branded Keywords
- _Learn Blogs
- __Blogspot
- __Wordpress
- Health
- Daily google Trending News
- Recipes
- Poetries
- Amazing Real Story
- _Cheate to Death
- __Attacked by nuclear
- __Selak – 7 times lucky
- __cheated death twice in 4 months.
- _The artist tetrachromat.
- Top 10 in the world
- Funny Celebreties
What is SEO: A Complete Guide to Search Engine Optimization
What-Is-SEO
Over the last few decades, the way businesses market their products and advertise their services has evolved rapidly. All thanks to the advent of the internet and its billion-plus users, brands have moved on from traditional marketing, and the attraction towards digital marketing has never been crazier before - presenting new job roles and career potentials. From content marketing to PPC, and social media marketing to SEO,
every aspect plays an equally important role. SEO, however, has a lot of aspects from on-page to off-page and backlinking to interlinking. Well, let's start with the basics first.
You’ve most likely heard the term before but may not have asked the question: What is SEO? We’re going to try and answer it regardless.What is SEO? Search Engine Optimization Explained
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of optimizing a website or webpage to increase the quantity and quality of its traffic from a search engine’s organic results.
How search engines work
Search engines are like libraries for the digital age.
Instead of storing copies of books, they store copies of web pages.
When you type a query into a search engine, it looks through all the pages in its index and tries to return the most relevant results.
To do this, it uses a computer program called an algorithm.
Nobody knows exactly how these algorithms work, but we do have clues, at least from Google.
Here’s what they say on their “How search works” page:
To give you the most useful information, Search algorithms look at many factors, including the words of your query, relevance and usability of pages, expertise of sources and your location and settings. The weight applied to each factor varies depending on the nature of your query – for example, the freshness of the content plays a bigger role in answering queries about current news topics than it does about dictionary definitions.
Speaking of Google, this is the search engine most of us use—at least for websearches. That’s because it has the most reliable algorithm by far.
That said, there are tons of other search engines you can optimize for.
Learn more about this in our guide to how search engines work.
How SEO works
In simple terms, SEO works by demonstrating to search engines that your content is the best result for the topic at hand.Precisely how you do this depends on the search engine you’re optimizing for.
If you want more organic traffic to your web pages, then you need to understand and cater to Google’s algorithm. If you want more video views, then it’s all about YouTube’s algorithm.
Since each search engine has a different ranking algorithm, it’d be impossible to cover them all in this guide.
So, going forward, we’ll focus on how to rank in the biggest search engine of them all: Google. FUN FACT Google has a market share of ~92%. That’s why it pays to optimize your website for Google instead of Bing, DuckDuckGo, or any other web search engine.
How to optimize for Google
Google famously uses more than 200 ranking factors.There was even talk way back in 2010 that there could be up to 10,000.
Nobody knows what all of these ranking factors are, but we do know some of them.
How? Because Google told us, and many people—including us—have studied the correlations between various factors and Google rankings.
We’ll discuss some of those shortly. But first, an important point:
Google ranks web pages, not web sites.
Just because your business makes stained glass windows doesn’t mean that every page on your site should rank for the query, “stained glass windows.”
You can rank for different keywords and topics with different pages.
Now let’s talk about some of the things that affect rankings and search engine visibility.
Crawlability
Before Google can even consider ranking your content, it first needs to know that it exists.Google uses several ways to discover new content on the web, but the primary method is crawling. To put it simply, crawling is where Google follows links on the pages they already know about to those they haven’t seen before. To do this, they use a computer program called a spider.
Let’s say that your homepage has a backlink from a website that’s already in Google’s index.
Next time they crawl that site, they’ll follow that link to discover your website’s homepage and likely add it to their index.
From there, they’ll crawl the links on your homepage to find other pages on your site.
That said, some things can block Google’s crawlers:
Poor internal linking: Google relies on internal links to crawl all the pages on your site. Pages without internal links often won’t get crawled.
Nofollowed internal links: Internal links with nofollow tags won’t get crawled by Google. Noindexed pages: You can exclude pages from Google’s index using a noindex meta tag or HTTP header. If other pages on your site only have internal links from noindexed pages, there’s a chance that Google won’t find them.
Blocks in robots.txt: Robots.txt is a text file that tells Google where it can and can’t go on your website. If pages are blocked here, it won’t crawl them.
If you’re concerned about any of these issues on your site, consider running an SEO audit with a tool like Ahrefs Site Audit.
Mobile-friendliness
63% of Google searches come from mobile devices, and that number is growing every year.Given that statistic, it probably comes as no surprise that in 2016, Google announced a ranking boost for mobile-friendly websites in its mobile search results.
Google also shifted to mobile-first indexing in 2018, meaning that they now use the mobile version of your page for indexing and ranking.
But here’s an even more critical statistic from Adobe:
Nearly 8 in 10 of consumers would stop engaging with content that doesn’t display well on their device.
In other words, most people will likely hit the back button when a desktop version of a site loads on mobile.
That’s important because Google wants to keep its users satisfied. Pages that aren’t optimized for mobile lead to dissatisfaction. And even if you do rank and win the click, most people won’t stick around to consume your content.
You can check if your web pages are mobile-friendly with Google’s mobile-friendly testing tool.
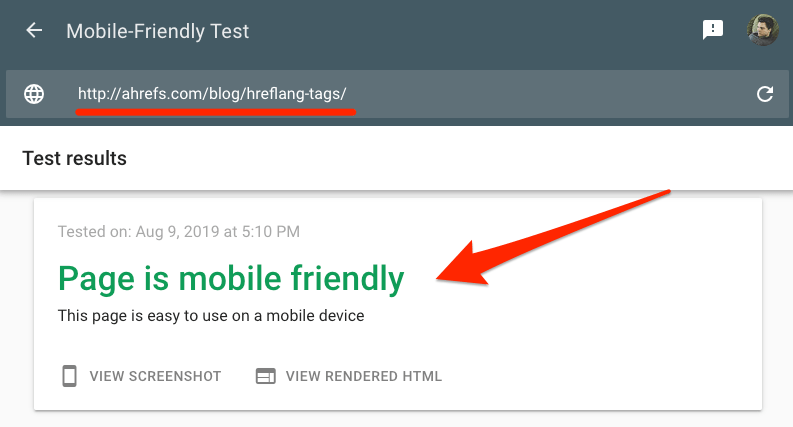
If they aren’t, hire a developer to fix them.
Pagespeed
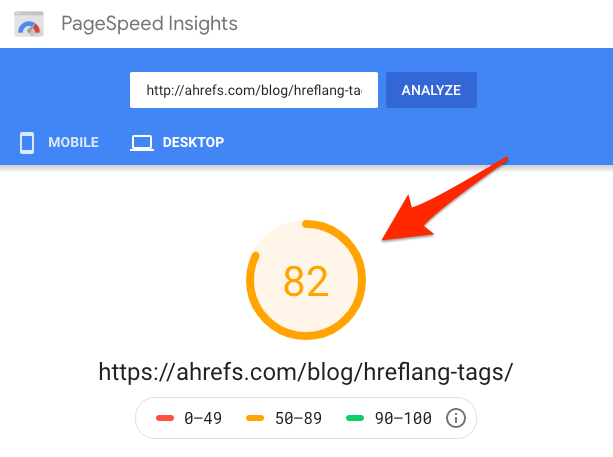
Pagespeed is how fast your page loads. It’s a ranking factor on desktop and mobile.Why? Once again, Google wants to keep its users satisfied. If their users are clicking on search results that take too long to load, that leads to dissatisfaction.
To check the speed of your web pages, use Google’s Pagespeed Insights tool. pagespeed insights 1
Search intent
Finding a keyword or keywords that you want to rank for is easy. Just paste a topic into a keyword research tool like Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, then look for relevant keyword ideas with search volume.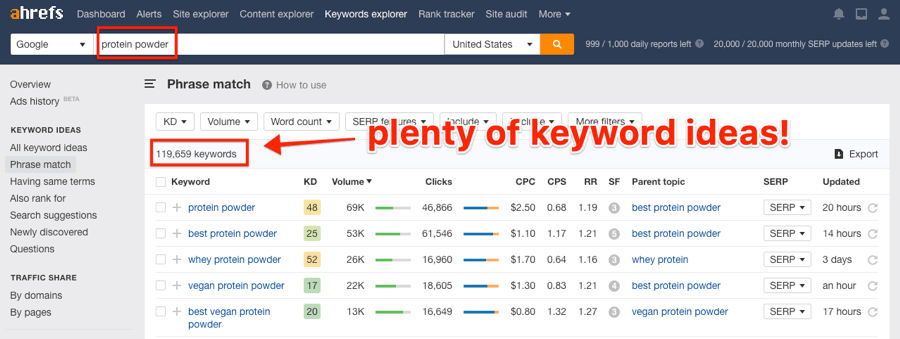
To demonstrate search intent, let’s look at an example.
Here are the current Google search results for the query “slow cooker recipes”:
slow cooker recipes 1
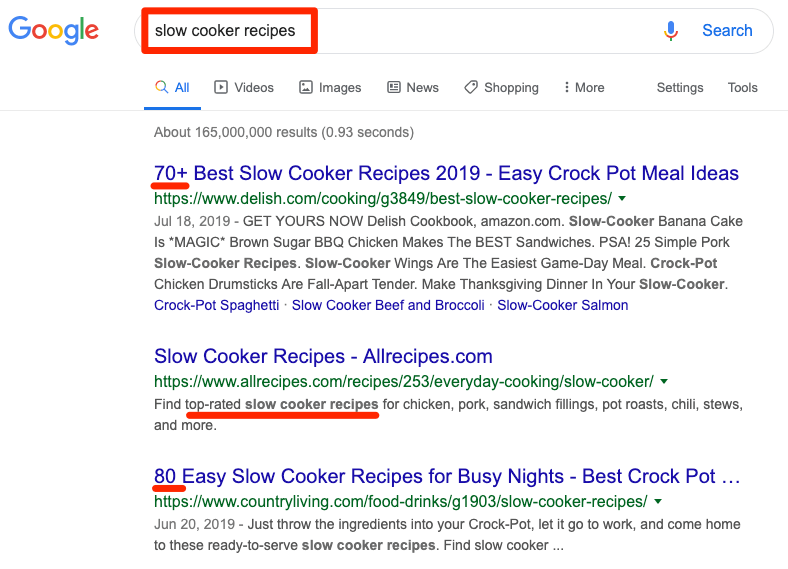
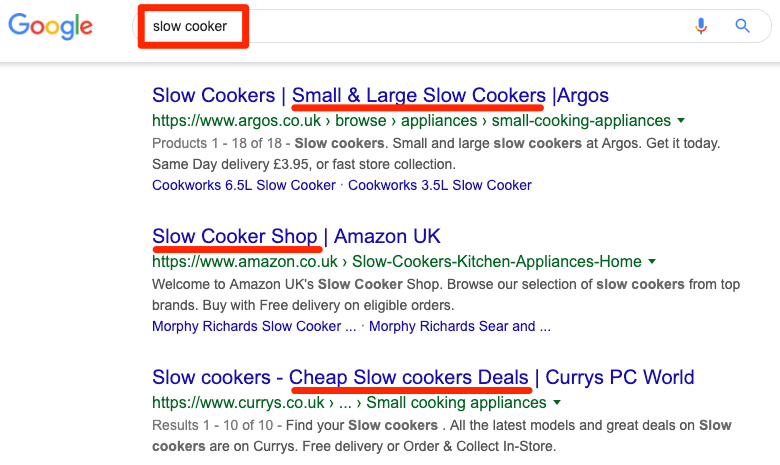
Google is interpreting the motive behind the query and showing the results the user wants to see. This is search intent in action.
How do you optimize for this?
Look at the top-ranking pages and ask yourself questions to identify the “3 C’s of search intent.”Content-type: Are most of the results blog posts, product pages, category pages, landing pages, or something else?
Content format: Is Google mainly ranking how-to guides, list-style articles, tutorials, comparisons, opinion pieces, or something entirely different? (Note. This one applies mainly to informational topics.)
Content angle: Is there a common theme or unique selling point across the top-ranking pages? If so, this gives you some insight into what might be important to searchers.
Beyond this, you can also check for the presence (or not) of SERP features to infer intent.
For example, if there’s a featured snippet in the results, then this may indicate that the searcher is looking for information.
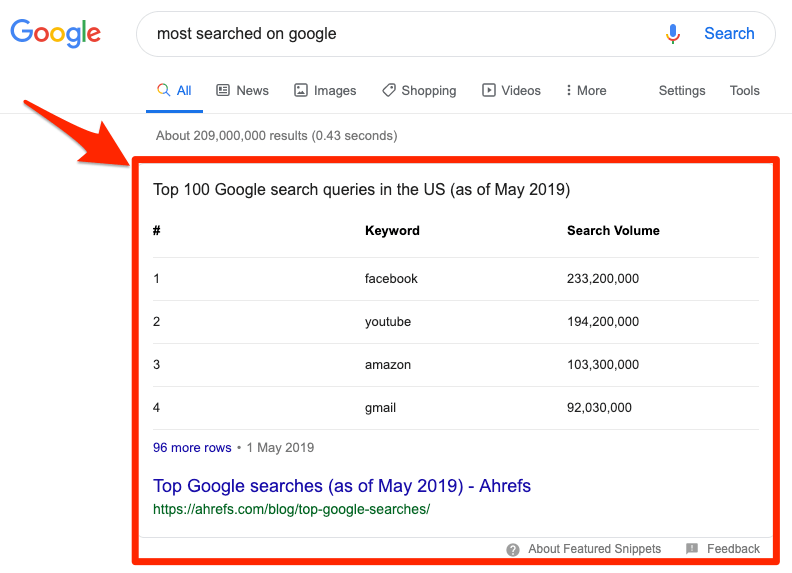
Recommended reading: What is Search Intent? A Complete Guide for Beginners
Backlinks
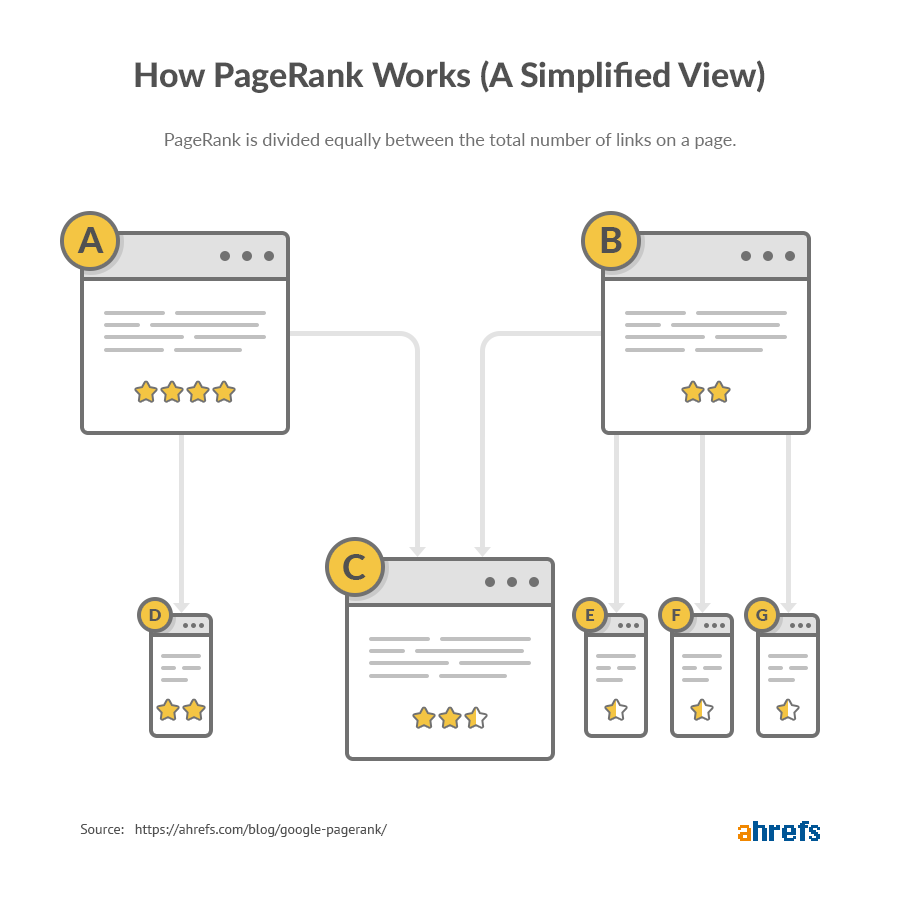
Google’s ranking algorithm is based on something called PageRank.
In simple terms, this interprets backlinks as votes. Generally speaking, pages with more votes tend to rank higher.
How do we know? Last year, we studied almost one billion web pages and found a clear correlation between referring domains (links from unique websites) and organic search traffic.
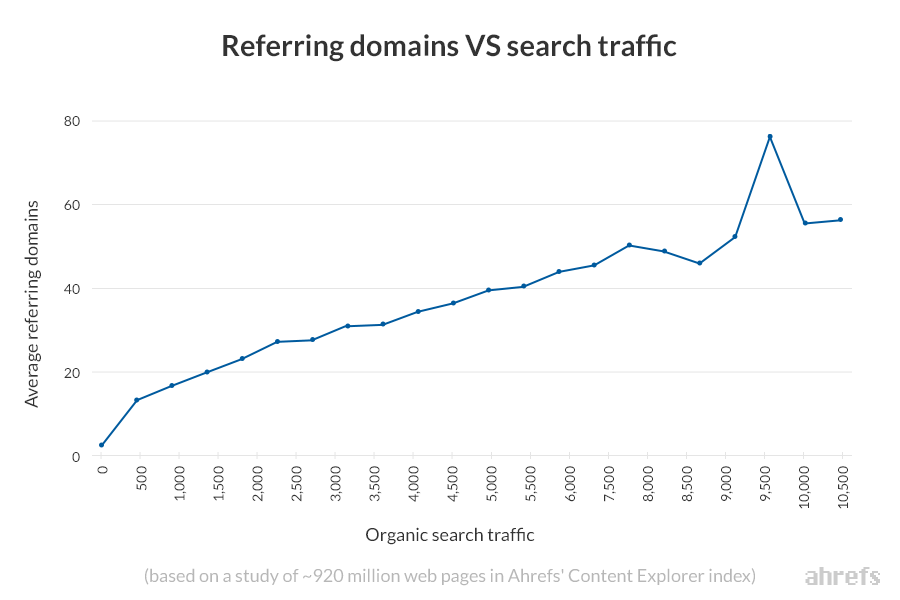
Long story short, backlinks matter if you want to rank for anything worthwhile.
The problem is that links can be challenging to build, especially to certain types of content like product pages.
There are tons of link-building tactics but if you’re new to the game, aim to build links to your best informational content (e.g., a blog post or a free tool).
Here’s one way to do that:Search for your target keyword on Google. Look for pages that aren’t as good as yours. Paste the URL of that page into our free backlink checker to see its top 100 links.
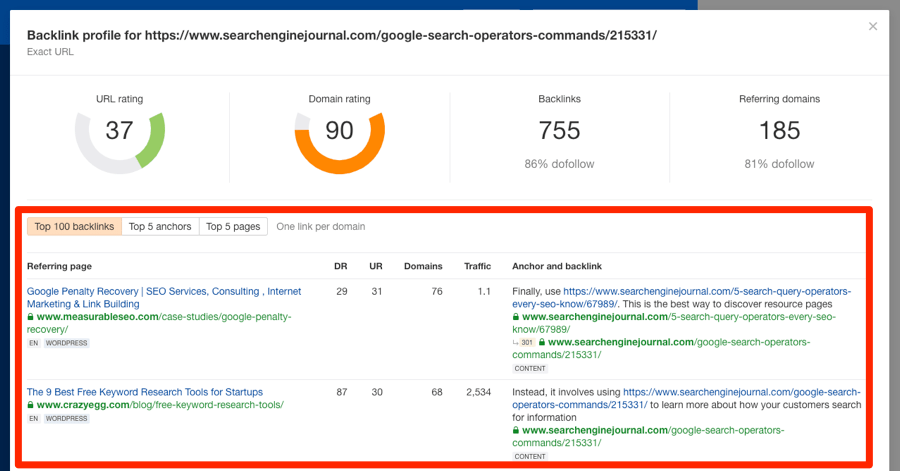
This tactic is commonly known as the Skyscraper Technique.
Unfortunately, Google discontinued public PageRank scores in 2016. That means there’s no longer any way to see how much “authority” a web page has in Google’s eyes.
Luckily, there are similar metrics around, one of which is Ahrefs URL Rating (UR).
URL Rating runs on a scale from 0–100 and takes into account both the quantity and quality of backlinks to a web page.
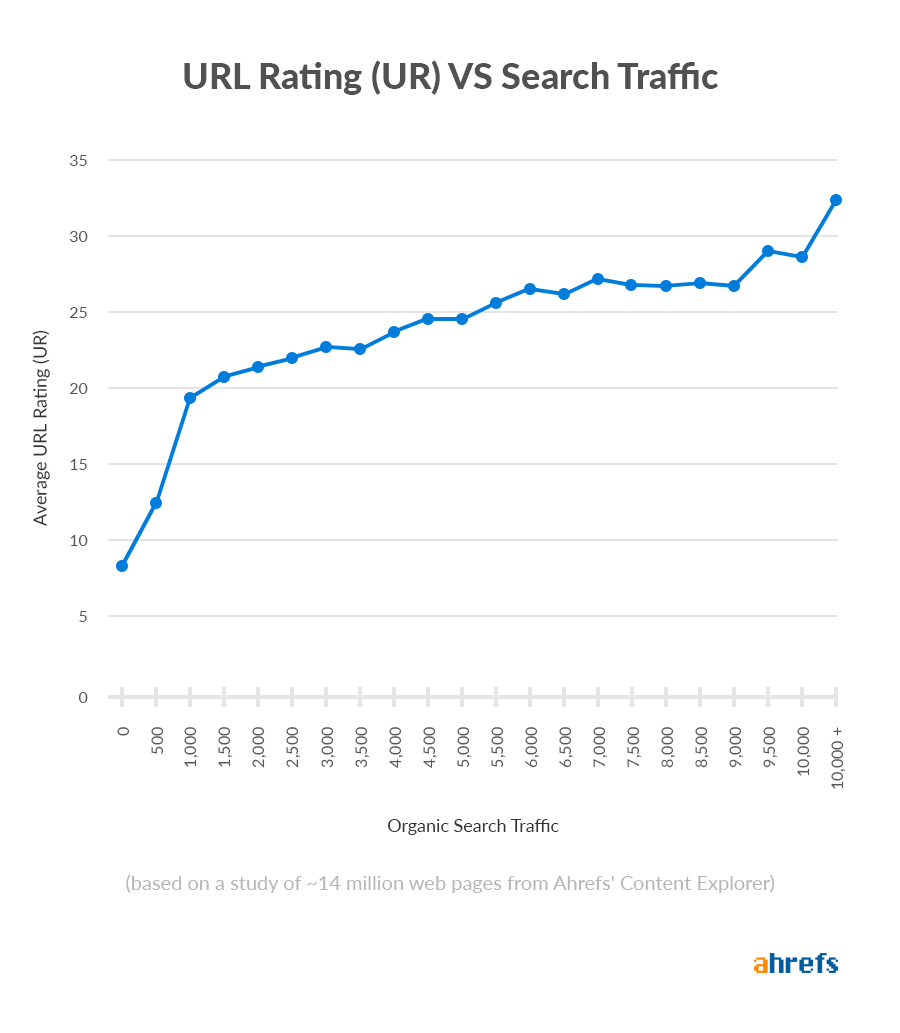
For that reason, when building backlinks to your content, you should prioritize the building of links from strong pages over weak ones.
If you’re analyzing competing pages for backlink opportunities in Ahrefs Site Explorer, the best way to do this is to look at the UR column in the “Backlinks” report.
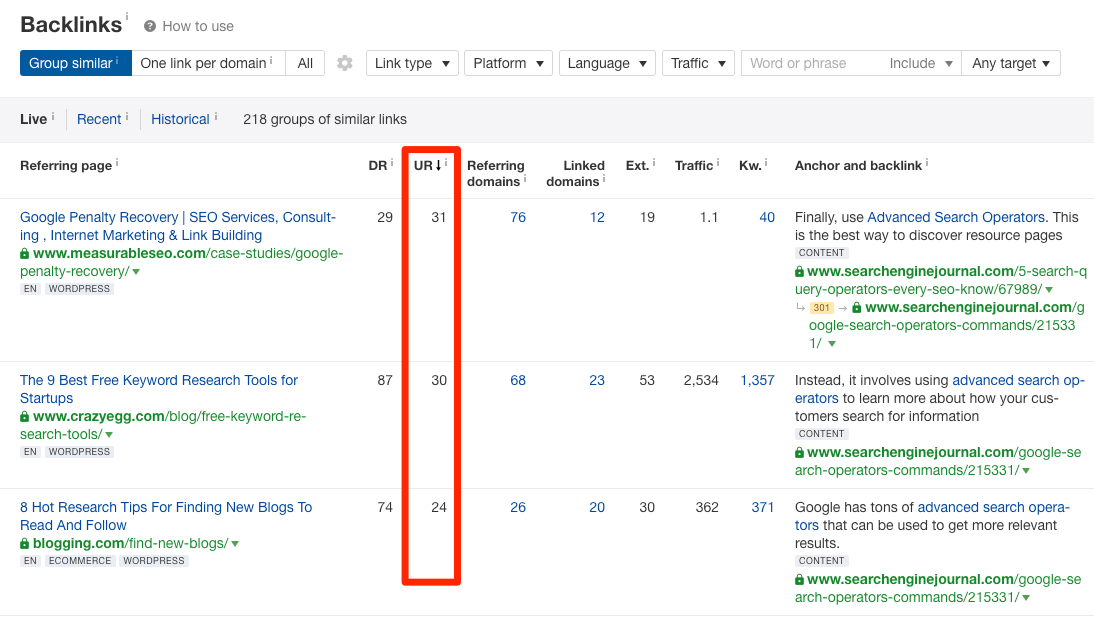
If you want to boost the “authority” of a particular page and are struggling to build backlinks to it, consider adding some relevant internal links from other high-authority pages.
To see your most authoritative pages, check the “Best By Links” report in Ahrefs Site Explorer.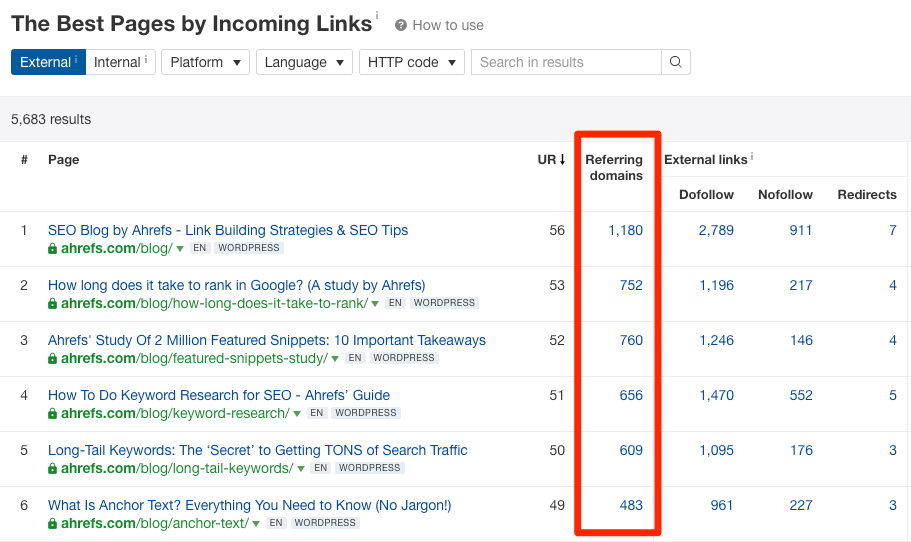
This tactic offers a good way to boost the “authority” of pages with commercial value like product pages. You’ll often struggle to build backlinks to those pages directly.
FURTHER READINGA Simple SEO Strategy for 2019 (The ‘Middleman’ Method)
Internal Links for SEO: An Actionable Guide
Content quality
Google wants to rank the most reliable and useful results—always.
To do this, they look at content-related signals like expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
Collectively, these are known as EAT.
(Learn more about EAT in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines.)
Other things you can do to increase the perceived quality of your content might be:
Stick to a 7th or 8th-grade reading level. Most Americans read at this level. Use short sentences and paragraphs. This is web content, not an essay.
Link to useful resources where appropriate. Don’t be concerned about “hoarding PageRank.” Aim to make your content as valuable to visitors as possible. Avoid big walls of text. Break things up with images, quotes, etc. Aim to make your content skimmable. Generally speaking, the more accessible your content is to the majority of searchers, the better.
Freshness is another important factor in some searches.For example, if you Google “best router,” you’ll see that almost all of the results were published or republished recently.
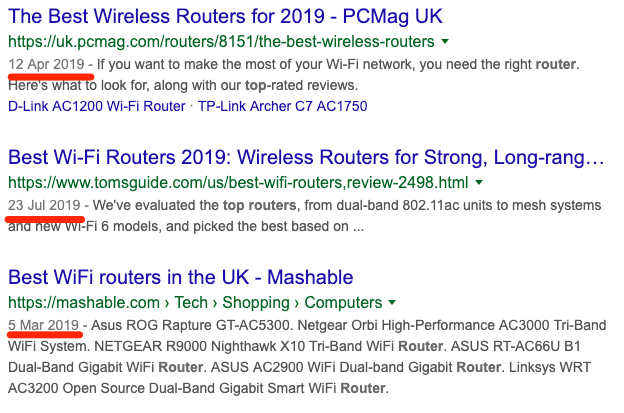
For other queries, freshness is less of a deciding factor.
Take a look at this top-ranking result for “how to tie a tie”:

Nobody has updated the page for over six years, but it doesn’t matter because the way you tie a tie is the same now as it was then.
Look at the search results for your target keyword to see whether freshness is seemingly an important ranking factor. Adjust your strategy as appropriate.
Why ranking is overrated… kind of Google looks at factors like location, past search history, and search settings to “tailor your results to what is most useful and relevant for you in that moment.”
That means even if you see your site ranking #1 for your target keyword, that might not be the case for everyone at all times.For example, if you search for “flapjack recipe” in the UK vs. the US, the results are different.
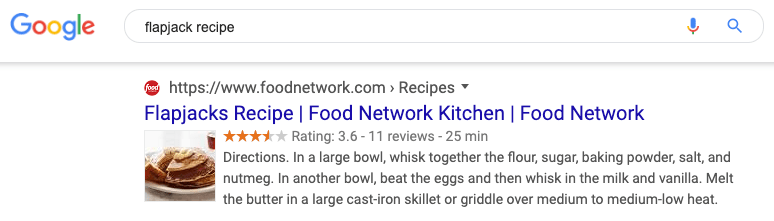
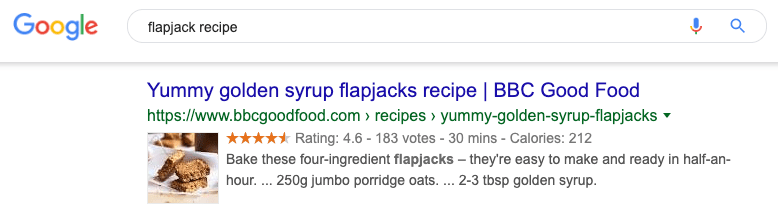
Alternatively, you can use a rank tracking tool like Ahrefs Rank Tracker to track keywords for a specific location—right down to the zip code. This is especially useful for local SEO.
Here are our rankings for “SEO audit” over the past year:
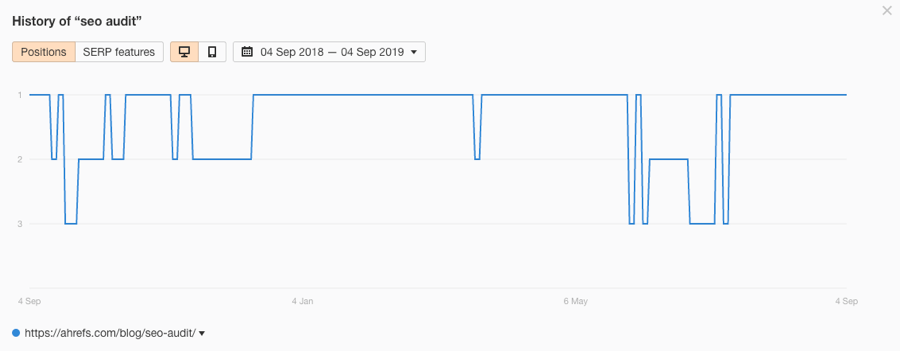
For that reason, it’s often better to pay more attention to organic traffic than rankings.
You can do this with analytics tools like Google Analytics, or you can get a rough estimate in Ahrefs Site Explorer.
Just paste in a URL, then go to the “Organic traffic” tab on the “Overview” report.
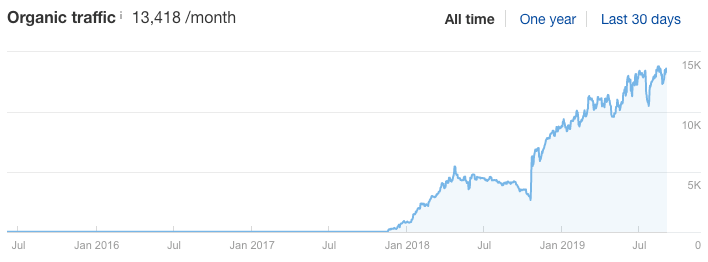
Or this:
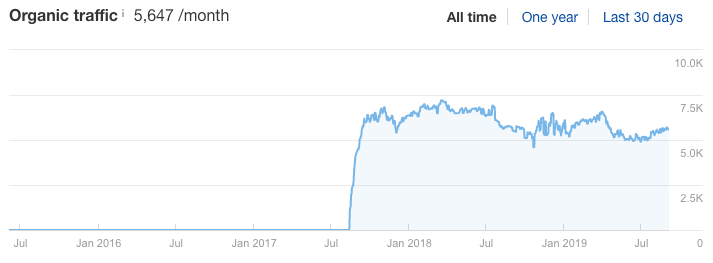
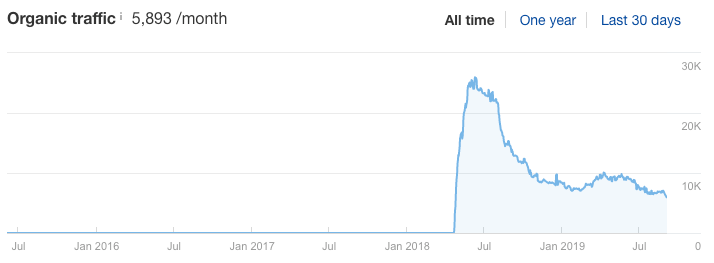
Not this:
What is White Hat SEO?
White Hat SEO typically refers to SEO tactics that are in tandem and agreement with the terms and conditions of the search engines. And just like the name suggests, white hat SEO is the contrast of black hat SEO. A white hat SEO practice like:
Creating original quality content and services Mobile-friendly website
Use of clear and keyword-rich meta tags
It will improve your search rankings on a SERP, and also maintain the integrity of your website.
If you want to rank for a particular keyword on Google, you need to apply SEO. There are two strategies for this:
On-page SEO Off-page SEO On-page SEO On-page SEO is the process of optimizing website elements. When you do this, there are certain factors that you need to take into account. All these elements are something that you can control as an end-user. The aspects of on-page SEO are:
Keyword Research Before you do anything with your website, the first thing you need to do is understand what keywords you want to rank for. To do this, you need to do keyword research. In this process, you choose the primary and secondary keywords around which you build meta tags and content.
The primary components for keyword research are:Search volume
Competition
Relevancy
You can also use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner and Ahrefs to search for keywords. Once you choose the keywords, you can go ahead and start optimizing your pages for those keywords.
Title Tag
The title tag is a header title element displaying the summary of your website's content on the search engine results page. It also influences click-through rates and is the most important factor in on-page SEO. Search engines display the first 50–60 characters of the title tag.
Meta Description A meta description is a brief description that summarizes the content of a webpage. They are also displayed on the search engine page results. In comparison to the title tag, a meta description gives users more understanding of what your webpage is about. Meta description also influences click-through rates.
But how do you optimize your content for SEO, and what “ranking factors” actually matter? To answer that, we first need to understand how search engines work.How search engines work Search engines are like libraries for the digital age.
Instead of storing copies of books, they store copies of web pages.
When you type a query into a search engine, it looks through all the pages in its index and tries to return the most relevant results.
To do this, it uses a computer program called an algorithm.Nobody knows exactly how these algorithms work, but we do have clues, at least from Google.
Here’s what they say on their “How search works” page:
To give you the most useful information, Search algorithms look at many factors, including the words of your query, relevance and usability of pages, expertise of sources and your location and settings. The weight applied to each factor varies depending on the nature of your query – for example,
the freshness of the content plays a bigger role in answering queries about current news topics than it does about dictionary definitions.
Speaking of Google, this is the search engine most of us use—at least for web searches. That’s because it has the most reliable algorithm by far.That said, there are tons of other search engines you can optimize for.
Learn more about this in our guide to how search engines work.
URL Structure
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. The best practice is to use SEO-friendly URLs, as they help to understand what the webpage is about. The poor URL structure is a big issue in SEO, which may result in your website getting lower ranks.
What is SEO: A Complete Guide to Search Engine Optimization Over the last few decades, the way businesses market their products and advertise their services has evolved rapidly.
All thanks to the advent of the internet and its billion-plus users, brands have moved on from traditional marketing, and the attraction towards digital marketing has never been crazier before - presenting new job roles and career potentials. From content marketing to PPC, and social media marketing to SEO, every aspect plays an equally important role. SEO,
however, has a lot of aspects from on-page to off-page and backlinking to interlinking. Well, let's start with the basics first. You’ve most likely heard the term before but may not have asked the question: What is SEO? We’re going to try and answer it regardless.What is SEO? Search Engine Optimization or SEO is the practice of increasing organic traffic on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP). It is also known as organic search or listings. If you want to rank number one for all the keywords, you need to apply SEO to increase your rank.
Suppose you started a blog for ice cream recipes, but your website doesn't rank high in the organic search results. There are several reasons why this can happen:Your competitors have better content
You use weak keywords
You use poor link building practices
Your webpage load time is slow
Your website doesn't have a good user experience
Your website is de-indexed by mistake
To rank high on the SERP, you need to understand how search engines work. In this article, you will learn about how Google ranks websites, the different types of SEO, and various SEO techniques you can use to improve your ranking.
What is Black Hat SEO?
Black hat SEO refers to the practices that violate the search engine's terms of service. It will likely increase a page's ranking in a search engine result page (SERP) for some time but can result in getting banned from search engines or affiliate sites since it's against the search engine's terms of service. Some of the black hat SEO techniques or practices include:
Keyword Stuffing Link Manipulation Creating articles, pages, or site landing pages with duplicate content Word of caution: You might experience short-term success. The traffic to your site might increase rapidly, but Google penalties are getting more sophisticated each passing day and can have crushing aftereffects both on your traffic and ranking.
What is White Hat SEO?
White Hat SEO typically refers to SEO tactics that are in tandem and agreement with the terms and conditions of the search engines. And just like the name suggests, white hat SEO is the contrast of black hat SEO. A white hat SEO practice like:
Creating original quality content and services Mobile-friendly website Use of clear and keyword-rich meta tags It will improve your search rankings on a SERP, and also maintain the integrity of your website.
Types of SEOIf you want to rank for a particular keyword on Google, you need to apply SEO. There are two strategies for this:
On-page SEO
Off-page SEO
On-page SEO
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing website elements. When you do this, there are certain factors that you need to take into account. All these elements are something that you can control as an end-user. The aspects of on-page SEO are:
Keyword Research Before you do anything with your website, the first thing you need to do is understand what keywords you want to rank for. To do this, you need to do keyword research. In this process, you choose the primary and secondary keywords around which you build meta tags and content.
The primary components for keyword research are: Search volume Competition Relevancy You can also use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner and Ahrefs to search for keywords. Once you choose the keywords, you can go ahead and start optimizing your pages for those keywords.Title Tag The title tag is a header title element displaying the summary of your website's content on the search engine results page. It also influences click-through rates and is the most important factor in on-page SEO. Search engines display the first 50–60 characters of the title tag.
Meta Description A meta description is a brief description that summarizes the content of a webpage. They are also displayed on the search engine page results. In comparison to the title tag, a meta description gives users more understanding of what your webpage is about. Meta description also influences click-through rates.
URL Structure URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. The best practice is to use SEO-friendly URLs, as they help to understand what the webpage is about. The poor URL structure is a big issue in SEO, which may result in your website getting lower ranks.
Header Tags Header tags help to identify the headings and subheadings of your content. The hierarchy of header tags goes from H1 to H6. H1 is the main heading of a page, the H2 tag is a subheading of H1, and so on. These tags help search engines to read and understand the content better.
Internal Link Internal links are links that link web pages together on your website. They allow users to navigate through the website. They are also useful to spread link equity (value passed from one website to another site).
Keyword Usage A search engine crawls a website using Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP helps search engines look for content and keywords.
For example: If your website is about digital marketing and you have used only the keyword “digital marketing” in it, then the chances of you ranking high for this keyword is low. It is important to add related keywords such as types of digital marketing, skills in digital marketing,
Sitemaps A sitemap is a way of organizing a website to help both users and search engines understand the structure of a website. There are two types of sitemaps:
HTML sitemaps: Designed for humans XML sitemaps: Designed for crawlers Now that you have a clear understanding of on-page SEO, let us discuss the off-page SEO section of the ‘What is SEO?’ article.
Off-page SEO Off-page SEO is another process of improving your rank on the search engine results page. It also helps to strengthen the credibility of your website and build a sense of domain authority and trustworthiness. Other benefits of off-page SEO are an increase in traffic, page rank, and brand awareness.
Link Building
Off-page SEO is mostly associated with link building. Link building is the process of acquiring hyperlinks from other websites to your site. This is also known as external link building. The key to link-building is always content. From an on-page SEO perspective, having quality content allows you to optimize it for relevant keywords and rank. From an off-page SEO strategy,
having high-quality content enables other sites to link back to your site.
Here are some strategies for link building: High-quality content creation - Other sites will link back to yours if your content is original, well-structured, and reads well. Off-site engagement - Spend a lot of time on other websites similar to yours. You can search for other sites that have relevant content.
You can share your content with them they can share their content with you. You can also achieve off-site engagement through social media and by collaborating with bloggers.
When learning ‘What is SEO’ there are also some do’s and don’ts as well which you should be aware of. The next section covers it.Master many facets of SEO including keyword research, technical SEO, link building, analytics, with the Search Engine Optimization training course.
Do's and Don'ts of SEO
Here are some important points to keep in mind for SEO.
DON'Ts
Opt for white hat techniques (basically all of the points mentioned above).
Do not opt for black hat techniques.
For example, choosing a keyword arbitrarily and stuffing that keyword into the content.
Try to get backlinks from relevant sites that have high-quality content.
Avoid backlinks from irrelevant sites.
Use keywords in your title tags, and have a unique title tag for multiple web pages.
Do not duplicate the same title tags on multiple web pages.
Write engaging content for a better user experience.
Do not plagiarize content.
Do keyword research. Understand the volume and competition for all the keywords.
Avoid keyword stuffing. Google will be able to pick up on this.
Build internal links to your website naturally.
Avoid building sitewide backlinks.
It takes time to rank your content so be patient and wait for a while.
Don't stress out and start using black hat techniques.
Make your website responsive and user-friendly across multiple devices.
Don't ignore mobile devices while making your website for the desktop. Most users today start their search process on their mobiles
SEO vs SEM Before we continue this ‘What is SEO?’ article, it’s worth addressing something many people get confused about — the difference between SEO vs SEM. Both are critical components of any successful digital marketing campaign, and SEO is actually a subset of SEM.
The main difference, which we go into much more detail here, is that SEM employs paid search engine advertising to target specific demographics.
How Does Google Rank Websites? Websites are ranked primarily based on the competition between your web pages and other web pages for a particular keyword. The web pages which follow the best practices outrank every other web page in the competition and rank on top for those keywords.
Search engines like Google follow three basic steps to rank a website. They are:Crawling
Search engines have spiders or bots which scans a website copies the entire website's content, and stores it in the search engine's index.
Indexing
Indexing is the method of adding web pages into Google search results. If your website is not in a search engine's index, no one will be able to find your website.
Ranking
When you type something in Google, the most relevant websites (from the index) will appear in the search results. These results are based on multiple factors like user location, language, experience, etc.
There are a lot of factors that go into ranking - relevancy being a critical aspect. For example, if you type Simplilearn, the web pages for Simplilearn shows up organically because they are relevant to that keyword. However, you also need to make sure that the page load time is fast for the end-user.
Google also takes into account other factors like how long someone stays on a website and the bounce rate (leaving the site after viewing only one page).
Language and location also play a vital role in ranking. For example, if you search in India, the results are going to be different than the results in the United States. This is because Google has different bots crawling different pages at different times and that Google's index is being updated continuously. However, it's not syncing in real-time.
To elaborate, if you search “cafes” while in San Francisco you're going to see different results. Now if you search for “cafes” while in Mumbai you're going to see different results.To sum it up, the most important factors for Google ranking are relevancy, user experience, language, and location.
Conclusion To make sure that your website stands out in the sea of millions of others move past the what is SEO stage and get moving on your SEO strategy. Simplilearn's Advanced Search Engine Optimization (SEO) course will help you turn into an industry-ready SEO professional from day one.
You will be able to master the many facets of SEO, including the process of organically driving traffic to your websites with keyword management and research, on-page and off-page optimization, link building, URL building, SEO analytics, and more and you'll acquire extensive project experience to prepare you for managing inbound marketing initiatives.
Final thoughts Knowing how search engines work and the attributes they’re looking for when ranking content is crucial when trying to create content that ranks.
That said, search engine algorithms change all the time and there’s no guarantee that what’s important today will still be important next year. Don’t let that panic you. Generally speaking, the important things stay consistent over time.
Factors like backlinks, “authority,” and matching search intent have been critical factors for many years—and there’s no sign of that changing any time soon.
Got questions? Leave a comment or ping me on Twitter. SIDENOTE. In the previous version of this post, we asked 40+ SEO industry experts to define SEO. Check out their definitions here.


0 Comments